AI开发-三方库-Hugging Face-Pipelines
1 需求
需求1:pipeline支持的任务类型
需求2:推理加速使用CPU还是GPU
需求3:基于pipeline的文本分类示例
需求4:pipeline实现原理
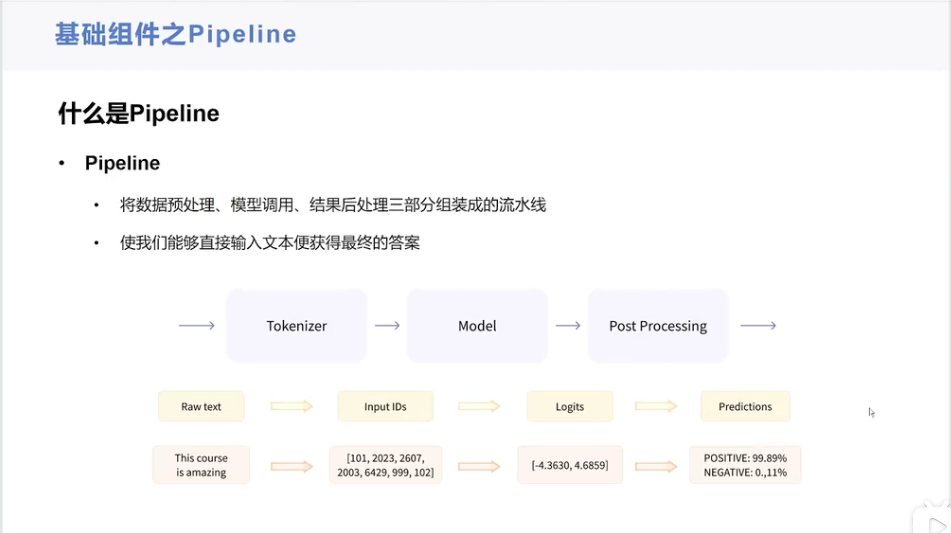

模型使用步骤(Raw text -》Input IDs -》Logits -》Predictions):
- 第一步:数据预处理(Raw text -》Input IDs)
- 第二步:模型调用(Input IDs -》Logits)
- 第三步:结果后处理(Logits -》Predictions)
以下是对这个流程的解释:
一、Raw text -> Input IDs
- 原始文本处理:
- “Raw text” 即原始文本,可能是一段自然语言的语句、文章段落等。
- 在自然语言处理任务中,首先需要将原始文本进行预处理,以便模型能够理解和处理。
- 分词与编码:
- 通常使用分词器(tokenizer)将原始文本分割成一个个的词或子词单元。例如,对于英文文本,可能会将单词拆分成词根、词缀等更小的单元;对于中文文本,可能会按照字、词等进行分割。
- 然后,分词器会为每个分割后的单元分配一个唯一的整数标识符,即 “Input IDs”。这些整数标识符可以被模型识别和处理。
- 例如,使用 Hugging Face 的 Transformers 库中的分词器,可以这样将原始文本转换为输入 ID 序列:
text = "今天天气不错"# 第一步:数据预处理(Raw text -》Input IDs)
from transformers import BertTokenizertokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('./model')
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True)
print(inputs)二、Input IDs -> Logits
- 模型处理输入:
- “Input IDs” 被输入到深度学习模型中,例如 Transformer 架构的语言模型。
- 模型会对输入的 ID 序列进行一系列的计算和处理,包括嵌入(embedding)、多头注意力(multi-head attention)、前馈神经网络(feed-forward neural network)等操作。
- 生成对数概率:
- 经过模型的计算,最终会输出一个向量,称为 “Logits”。Logits 是模型对每个可能的输出类别的对数概率。
- 例如,在文本分类任务中,如果有两个类别(正面和负面),那么 Logits 可能是一个长度为 2 的向量,分别表示输入文本属于正面类别和负面类别的对数概率。
- 以下是一个简单的示例,使用预训练的模型生成 Logits:
# 第二步:模型调用(Input IDs -》Logits)
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassificationmodel = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('./model')
# print(model.config)
outputs = model(**inputs)
logits = outputs.logits
print(logits)三、Logits -> Predictions
- 概率计算与预测:
- “Logits” 通常是未经过处理的对数概率,需要进一步转换为概率值。可以使用 softmax 函数将 Logits 转换为概率分布。
- Softmax 函数会将每个对数概率转换为一个介于 0 和 1 之间的概率值,并且所有概率值之和为 1。
- 然后,根据概率分布,可以选择概率最高的类别作为模型的预测结果。
- 例如:
# 第三步:结果后处理(Logits -》Predictions)
import torchpredictions = torch.nn.functional.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
predictions_class = torch.argmax(predictions).item()
print(predictions_class)
print(model.config.id2label.get(predictions_class))这个流程是自然语言处理中常见的文本分类任务的基本步骤,不同的任务和模型可能会有所不同,但总体上都遵循这个从原始文本到最终预测的过程。
2 接口
关键参数
- task:指定任务类型
- model:指定模型
- tokenizer:指定分词器
- device:指定使用GPU进行推理加速
常见调用方式
- pipeline(task="text-classification")
- pipeline(task="text-classification", model="./model")
- pipeline(task="text-classification", model="./model", tokenizer="./model")
- pipeline(task="text-classification", model="./model", tokenizer="./model", device=-1)


3.1 支持任务类型
from transformers.pipelines import SUPPORTED_TASKSfor k, v in SUPPORTED_TASKS.items():print(k)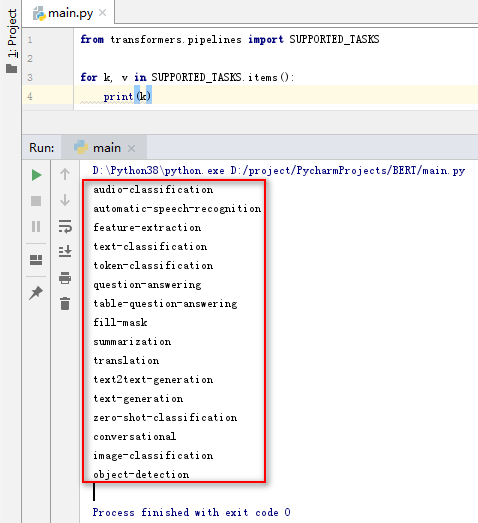

3.2 推理加速使用CPU还是GPU
from transformers import pipelinepipe = pipeline(task="text-classification", model="./model", tokenizer="./model")print(pipe.model.device)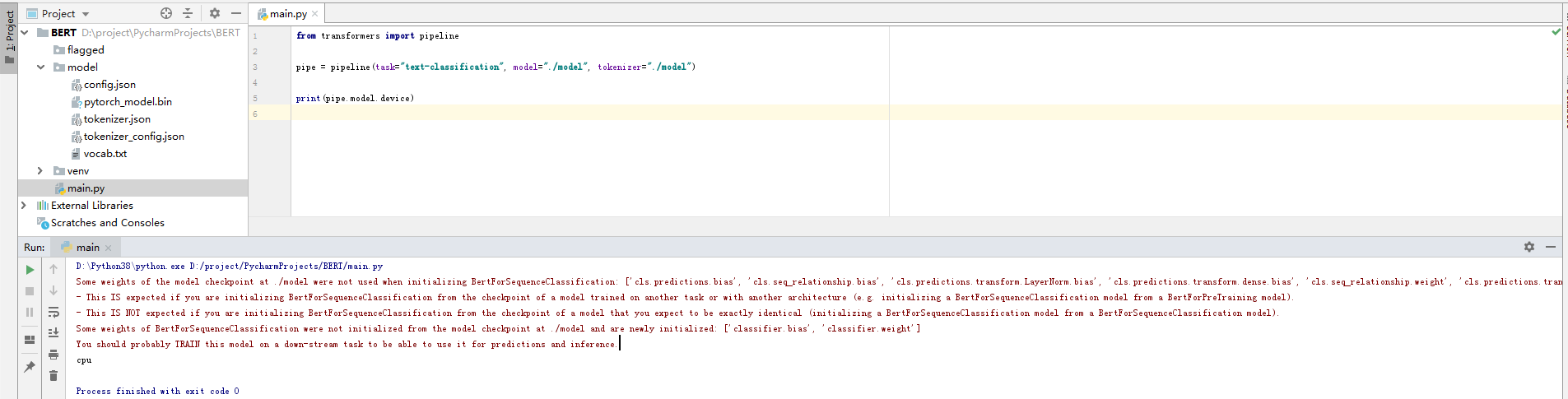
3.3 基于pipeline的文本分类示例
from transformers import pipelinepipe = pipeline(task="text-classification", model="./model", tokenizer="./model", device=-1)
result = pipe("今天天气不错")
print(result)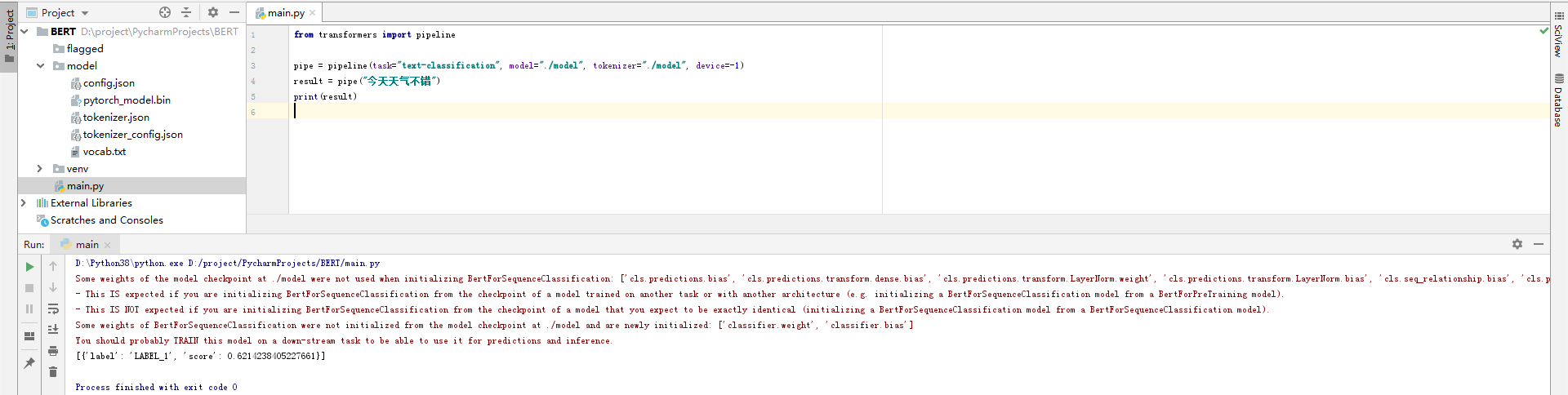
3.4 pipeline实现原理
text = "今天天气不错"# 第一步:数据预处理(Raw text -》Input IDs)
from transformers import BertTokenizertokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('./model')
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors='pt', padding=True, truncation=True)
print(inputs)# 第二步:模型调用(Input IDs -》Logits)
from transformers import BertForSequenceClassificationmodel = BertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('./model')
# print(model.config)
outputs = model(**inputs)
logits = outputs.logits
print(logits)# 第三步:结果后处理(Logits -》Predictions)
import torchpredictions = torch.nn.functional.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
predictions_class = torch.argmax(predictions).item()
print(predictions_class)
print(model.config.id2label.get(predictions_class))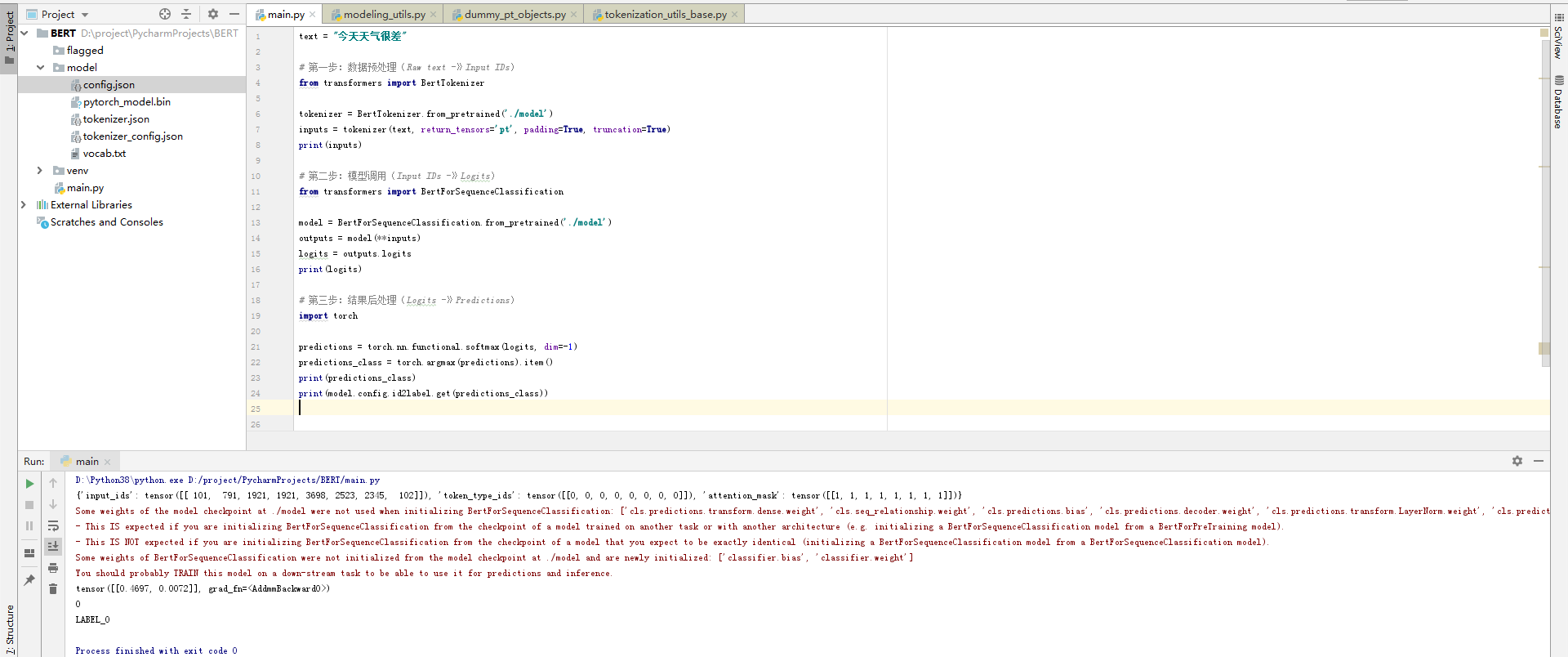
4 参考资料
https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/pipelines
https://hf-mirror.com/docs/transformers/main_classes/pipelines
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_48007632/category_12725843.html
