ffmpeg面向对象——拉流协议匹配机制探索
目录
- 1.URLProtocol类
- 2.协议匹配的核心接口
- 3. URLContext类
- 4. 综合调用流程图
- 5.rtsp拉流协议匹配流程图及对象图
- 5.1 rtsp拉流协议调用流程图
- 5.2 rtsp拉流协议对象图
- 6.本地文件调用流程图及对象图
- 6.1 本地文件调用流程图
- 6.2 本地文件对象图
- 7.内存数据调用流程图及对象图
- 7.1 内存数据调用流程图
- 7.2 内存数据对象图
- 8 filename取值规则
- 9.小结
如果让你写个拉流程序,输入拉流地址,可以是本地文件路径,可以是内存数据,可以网络流媒体传输协议比如http或者rtsp等,那么不同拉流地址 ,调用底层的读写函数不一样,如何统一操作呢?探索下ffmpeg是怎么统一这种问题的。
ffmpeg抽象出了url协议类——URLProtocol类——来统一这种操作。
(雷神有画出使用时的各个协议雷神相关博客,但是没有看到其匹配机制,且只有函数调用图,没有对象图。我这个探索,可以算是补充)
1.URLProtocol类
typedef struct URLProtocol {const char *name;int (*url_open)( URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags);/*** This callback is to be used by protocols which open further nested* protocols. options are then to be passed to ffurl_open_whitelist()* or ffurl_connect() for those nested protocols.*/int (*url_open2)(URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);int (*url_accept)(URLContext *s, URLContext **c);int (*url_handshake)(URLContext *c);/*** Read data from the protocol.* If data is immediately available (even less than size), EOF is* reached or an error occurs (including EINTR), return immediately.* Otherwise:* In non-blocking mode, return AVERROR(EAGAIN) immediately.* In blocking mode, wait for data/EOF/error with a short timeout (0.1s),* and return AVERROR(EAGAIN) on timeout.* Checking interrupt_callback, looping on EINTR and EAGAIN and until* enough data has been read is left to the calling function; see* retry_transfer_wrapper in avio.c.*/int (*url_read)( URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size);int (*url_write)(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size);int64_t (*url_seek)( URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence);int (*url_close)(URLContext *h);int (*url_read_pause)(URLContext *h, int pause);int64_t (*url_read_seek)(URLContext *h, int stream_index,int64_t timestamp, int flags);int (*url_get_file_handle)(URLContext *h);int (*url_get_multi_file_handle)(URLContext *h, int **handles,int *numhandles);int (*url_get_short_seek)(URLContext *h);int (*url_shutdown)(URLContext *h, int flags);const AVClass *priv_data_class;int priv_data_size;int flags;int (*url_check)(URLContext *h, int mask);int (*url_open_dir)(URLContext *h);int (*url_read_dir)(URLContext *h, AVIODirEntry **next);int (*url_close_dir)(URLContext *h);int (*url_delete)(URLContext *h);int (*url_move)(URLContext *h_src, URLContext *h_dst);const char *default_whitelist;
} URLProtocol;这其实就是高级语言(如c++等)的接口类——需要各个子类实现的接口。
可以看到,这类,抽象出来的共性的接口——读写文件等。如果是本地文件,那就调用fopen等系统调用,如果是内存数据则调用用户自定义的读取函数,如果是网络流媒体协议,则是调用socket网络编程接口——这样实现了多态。
因此,ffmpeg实例化了很多它支持的URLProtocol类对象,放到了全局表格url_protocols中,比如
//在libavformat/protocol_list.c
static const URLProtocol *url_protocols[] = {&ff_file_protocol,&ff_hls_protocol,&ff_http_protocol,&ff_httpproxy_protocol,&ff_rtmp_protocol,&ff_rtmpt_protocol,&ff_rtp_protocol,&ff_srtp_protocol,&ff_tcp_protocol,&ff_udp_protocol,&ff_unix_protocol,NULL };注意:protocol_list.c是configure生成的,也就是说下载的ffmpeg源码中是不存在的,这个是ffmpeg可裁剪的一个举措。——可以配置configure来选择支持哪些协议,和linux的menuconfig类似(不得不觉得互相学习)。
和这篇《ffmpeg面向对象-rtsp拉流相关对象》探索过的ffmpeg统一输入格式的方式一样。这个可以说是ffmpeg的特点的,一个开源项目有其遵循的法则,指定的规则,通一知百。
2.协议匹配的核心接口
ffmpeg实现协议匹配的核心接口是url_find_protocol。
#define URL_SCHEME_CHARS \"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" \"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" \"0123456789+-."static const struct URLProtocol *url_find_protocol(const char *filename)
{const URLProtocol **protocols;char proto_str[128], proto_nested[128], *ptr;size_t proto_len = strspn(filename, URL_SCHEME_CHARS);int i;if (filename[proto_len] != ':' &&(strncmp(filename, "subfile,", 8) || !strchr(filename + proto_len + 1, ':')) ||is_dos_path(filename))strcpy(proto_str, "file");elseav_strlcpy(proto_str, filename,FFMIN(proto_len + 1, sizeof(proto_str)));av_strlcpy(proto_nested, proto_str, sizeof(proto_nested));if ((ptr = strchr(proto_nested, '+')))*ptr = '\0';protocols = ffurl_get_protocols(NULL, NULL);if (!protocols)return NULL;for (i = 0; protocols[i]; i++) {const URLProtocol *up = protocols[i];if (!strcmp(proto_str, up->name)) {av_freep(&protocols);return up;}if (up->flags & URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NESTED_SCHEME &&!strcmp(proto_nested, up->name)) {av_freep(&protocols);return up;}}av_freep(&protocols);if (av_strstart(filename, "https:", NULL) || av_strstart(filename, "tls:", NULL))av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "https protocol not found, recompile FFmpeg with ""openssl, gnutls or securetransport enabled.\n");return NULL;
}
可以看到,它先判断传入的filename是文件路径还是流传输url,前者把proto_str设为“file”,后者取url的传输协议头比如“tcp”设给proto_str。
ffurl_get_protocols主要是获取url_protocols表格里的各个协议类对象地址(内部做了次拷贝,反正不用管)。
再for遍历比较proto_str和各个协议类对象的name是否相同,这样就从url_protocols协议表格中匹配到对应协议类对象了。
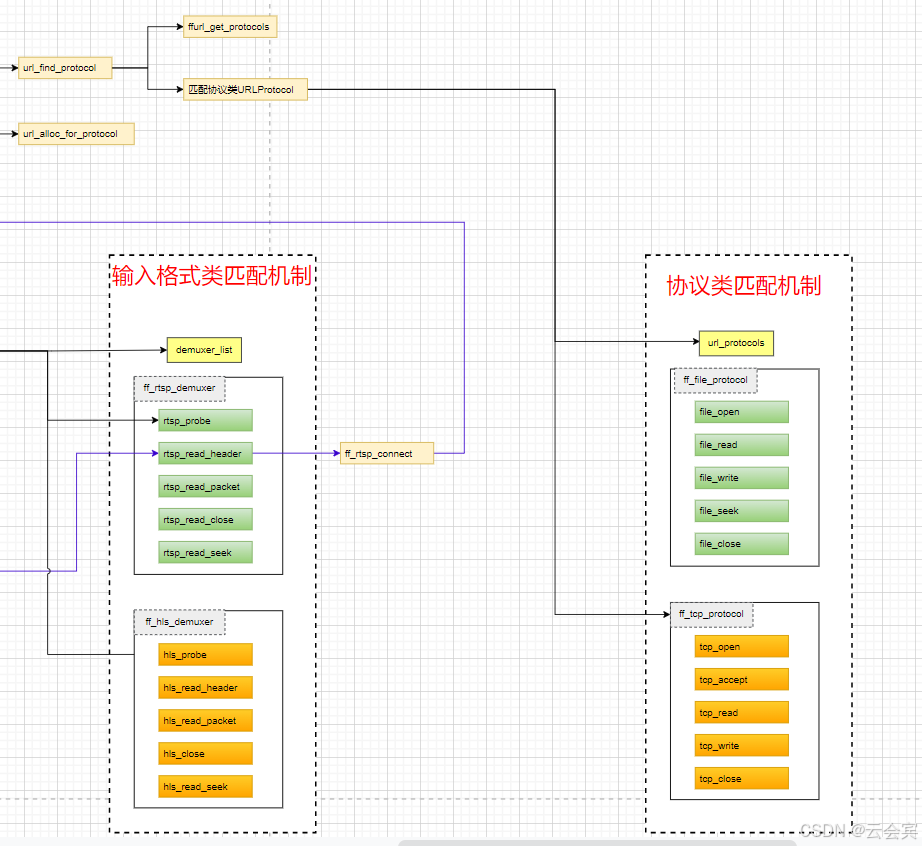
其实到这里,匹配机制完毕,接下来就是追踪调用源头。
这个匹配函数最后返回对应协议类对象的地址——这个地址给谁了呢?这得看谁调它了,调它的有两处,一个是ffurl_alloc(),一个是avio_find_protocol_name。前者取匹配到的协议对象地址,后者是取协议对象的名字,显而易见,前者是比较重要的。
int ffurl_alloc(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb)
{const URLProtocol *p = NULL;p = url_find_protocol(filename);if (p)return url_alloc_for_protocol(puc, p, filename, flags, int_cb);*puc = NULL;return AVERROR_PROTOCOL_NOT_FOUND;
}可以看到,协议类对象地址作为形参传给url_alloc_for_protocol函数了,看其最终到哪里了?
static int url_alloc_for_protocol(URLContext **puc, const URLProtocol *up,const char *filename, int flags,const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb)
{URLContext *uc;int err;……uc = av_mallocz(sizeof(URLContext) + strlen(filename) + 1);if (!uc) {err = AVERROR(ENOMEM);goto fail;}uc->av_class = &ffurl_context_class;uc->filename = (char *)&uc[1];strcpy(uc->filename, filename);uc->prot = up;uc->flags = flags;uc->is_streamed = 0; /* default = not streamed */uc->max_packet_size = 0; /* default: stream file */……
}
剔除无关代码后,可以看到最终是放到URLContext类对象的prot成员中——看来URLContext类是URLProtocol 类的管理者。
3. URLContext类
此时对象图如下:

URLContext协议上下文类来管理匹配到的协议类。其URLContext类定义如下
typedef struct URLContext {const AVClass *av_class; /**< information for av_log(). Set by url_open(). */const struct URLProtocol *prot;void *priv_data;char *filename; /**< specified URL */int flags;int max_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this max packet size */int is_streamed; /**< true if streamed (no seek possible), default = false */int is_connected;AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;int64_t rw_timeout; /**< maximum time to wait for (network) read/write operation completion, in mcs */const char *protocol_whitelist;const char *protocol_blacklist;int min_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this min packet size */
} URLContext;可以发现,它第一个成员是AVClass 的指针成员,此时(url_alloc_for_protocol函数处理后),指向了ffurl_context_class,《ffmpeg面向对象——参数配置机制及其设计模式探索》探索过,凡是戴上这个帽子的,它就成为了可配参数业务类,不再赘述。可见它的可配的参数就3个,如下

白名单,黑名单,读写超时时间。最终是设置到这个协议管理类里了。
4. 综合调用流程图
那么又是谁调用ffurl_alloc的呢?
看到被调用的地方有很多,但是 ffurl_open_whitelist 是个关键调用——它是内存数据、本地文件或者流媒体协议最终都会调用的。
具体如何调用的,见如下综合调用流程。

到此,协议匹配探索到源头,算是结束。
但是这个综合图把所有情况都考虑到了,但是这样很不好,很不清晰,鼻子眉毛一把抓,非常不清晰,不易于理解。应该分解下,根据业务功能单独画。
对于庞大代码,业务功能融合多的代码,要用业务线索来看——从单一的业务功能点为聚焦点,这样别的业务代码不会迷了眼,就像《ffmpeg面向对象——参数配置机制及其设计模式探索》一样,只聚焦于参数流向,无关代码,让开。
因此,按业务功能点可以拆分成网络流媒体协议匹配、本地文件路径匹配和内存数据匹配等3大块。网络流媒体协议常用的rtsp等是个代表。
5.rtsp拉流协议匹配流程图及对象图
5.1 rtsp拉流协议调用流程图
rtsp协议下,它匹配到的协议调用流程如下:

剔除了其他业务流程,瞬间干净清爽许多。
可以看到rtsp的协议匹配触发在输入格式的方法里。
5.2 rtsp拉流协议对象图
其对象图如下:

图上最下面的就是这个协议管理类URLContext 了(对象图上已标注出其匹配到的全局变量了)。
在rtsp拉流协议下,URLContext作为的输入格式AVInputFormat中私有数据的成员,比如rtsp的私有数据RTSPState。
typedef struct RTSPState {const AVClass *class; /**< Class for private options. */URLContext *rtsp_hd; /* RTSP TCP connection handle *//** number of items in the 'rtsp_streams' variable */int nb_rtsp_streams;struct RTSPStream **rtsp_streams; /**< streams in this session *//** indicator of whether we are currently receiving data from the* server. Basically this isn't more than a simple cache of the* last PLAY/PAUSE command sent to the server, to make sure we don't* send 2x the same unexpectedly or commands in the wrong state. */enum RTSPClientState state;……}
6.本地文件调用流程图及对象图
6.1 本地文件调用流程图
待探索。
6.2 本地文件对象图
待探索。
7.内存数据调用流程图及对象图
7.1 内存数据调用流程图
待探索。
7.2 内存数据对象图
待探索。
8 filename取值规则
ffmpeg封装的基础接口是url_find_protocol的形参filename取值范围,前面没说,为了过流程,就忽略了。
拿url_protocols表格中ffmpeg支持的几个url协议上,探索下这个filename的取值范围是啥。
const URLProtocol ff_file_protocol = {.name = "file",.url_open = file_open,.url_read = file_read,.url_write = file_write,.url_seek = file_seek,.url_close = file_close,.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,.url_check = file_check,.url_delete = file_delete,.url_move = file_move,.priv_data_size = sizeof(FileContext),.priv_data_class = &file_class,.url_open_dir = file_open_dir,.url_read_dir = file_read_dir,.url_close_dir = file_close_dir,.default_whitelist = "file,crypto,data"
};const URLProtocol ff_hls_protocol = {.name = "hls",.url_open = hls_open,.url_read = hls_read,.url_close = hls_close,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NESTED_SCHEME,.priv_data_size = sizeof(HLSContext),
};const URLProtocol ff_tcp_protocol = {.name = "tcp",.url_open = tcp_open,.url_accept = tcp_accept,.url_read = tcp_read,.url_write = tcp_write,.url_close = tcp_close,.url_get_file_handle = tcp_get_file_handle,.url_get_short_seek = tcp_get_window_size,.url_shutdown = tcp_shutdown,.priv_data_size = sizeof(TCPContext),.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,.priv_data_class = &tcp_class,
};const URLProtocol ff_udp_protocol = {.name = "udp",.url_open = udp_open,.url_read = udp_read,.url_write = udp_write,.url_close = udp_close,.url_get_file_handle = udp_get_file_handle,.priv_data_size = sizeof(UDPContext),.priv_data_class = &udp_class,.flags = URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK,
};从这些支持的协议类型看,filename的取值范围其实就是在这些协议类对象里,那么代码里怎么知道是哪个呢?不同协议类型的name是不一样的,比如上面的有"udp"、“tcp”、"file"等等,就是filename传递进来的时候肯定是有处理过的,那么在哪里处理比价合理呢?在各个业务功能模块里比较合理。比如rtsp拉流协议的输入格式AVInputFormat(网上称之解复用器,其实我觉得叫复合数据分离器比较贴切,demux我一直翻译成分离器比较容易理解,一分多,mux融合数据,多合一)里rtsp_read_header这个回调里调用的ff_rtsp_connect中,进行了处理:

可以看到,会把rtsp拉流url比如“rtsp://ip:port/xxx”给改成“tcp://ip:port/xxx”,这样在url_find_protocol中就能截取到“tcp”从而rtsp的拉流协议会匹配到ff_tcp_protocol。
其他类似,肯定有处理的地方。
9.小结
和ffmpeg的输入格式统一到一个类和一个表格一样,这个拉流协议匹配也是统一到一个类和一个表格,且都是configure可裁剪的。及其相似,同类规则,我相信其他模块也是类似。
其实应该倒看,章节倒看会比较不错,比如5-4-3-2-1或者6-4-3-2-1或者7-4-3-2-1。
