阻塞队列相关的问题
阻塞队列相关的问题
1. 阻塞队列
阻塞队列(BlockingQueue)是一个支持两个附加操作的队列。这两个附加的操作是:
在队列为空时,获取元素的线程会等待队列变为非空。当队列满时,存储元素的线程会等
待队列可用。阻塞队列常用于生产者和消费者的场景,生产者是往队列里添加元素的线程,
消费者是从队列里拿元素的线程。阻塞队列就是生产者存放元素的容器,而消费者也只从
容器里拿元素。
1.ArrayBlockingQueue
ArrayBlockingQueue 是一个由数组支持的有界缓存的阻塞队列。在读写操作上都需要
锁住整个容器,因此吞吐量与一般的实现是相似的,适合于实现“生产者消费者”模式。
ArrayBlockingQueue 内部还保存着两个整形变量,分别标识着队列的头部和尾部在数组中
的位置。这个类是线程安全的。生产者和消费者共用一把锁。
源码:
/** The queued items */
final Object[] items;
/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
int takeIndex;
/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
int putIndex;
/** Number of elements in the queue */
int count;
/** Main lock guarding all access */
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull;public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {if (capacity <= 0)throw new IllegalArgumentException();this.items = new Object[capacity];lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);notEmpty = lock.newCondition();notFull = lock.newCondition();
}private void enqueue(E x) {// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;// assert items[putIndex] == null;final Object[] items = this.items;items[putIndex] = x;if (++putIndex == items.length)putIndex = 0;count++;notEmpty.signal();
}private E dequeue() {// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;// assert items[takeIndex] != null;final Object[] items = this.items;@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")E x = (E) items[takeIndex];items[takeIndex] = null;if (++takeIndex == items.length)takeIndex = 0;// 循环队列count--;if (itrs != null)itrs.elementDequeued();notFull.signal();return x;
}public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {checkNotNull(e);final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count == items.length)notFull.await();enqueue(e);} finally {lock.unlock();}
}public E take() throws InterruptedException {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count == 0)notEmpty.await();return dequeue();} finally {lock.unlock();}
}public boolean offer(E e) {checkNotNull(e);final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {if (count == items.length)return false;else {enqueue(e);return true;}} finally {lock.unlock();}
}public E poll() {final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;lock.lock();try {return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();} finally {lock.unlock();}
}2.LinkedBlockingQueue
基于链表的阻塞队列,内部维持着一个数据缓冲队列(该队列由链表构成)。
只有当队列缓冲区达到最大值缓存容量时(LinkedBlockingQueue 可以通过构造函数
指定该值),才会阻塞生产者线程,直到消费者从队列中消费掉一份数据,生产者线程会
被唤醒,反之对于消费者这端的处理也基于同样的原理。
LinkedBlockingQueue 之所以能够高效的处理并发数据,还因为其对于生产者端和消
费者端分别采用了独立的锁来控制数据同步,这也意味着在高并发的情况下生产者和消费
者可以并行地操作队列中的数据,以此来提高整个队列的并发性能。
源码:
/** The capacity bound, or Integer.MAX_VALUE if none */
private final int capacity;
/** Current number of elements */
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
/**
* Head of linked list.
* Invariant: head.item == null
*/
transient Node<E> head;
/**
* Tail of linked list.
* Invariant: last.next == null
*/
private transient Node<E> last;
/** Lock held by take, poll, etc */
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting takes */
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
/** Lock held by put, offer, etc */
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
/** Wait queue for waiting puts */
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert last.next == null;last = last.next = node;
}private E dequeue() {// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();// assert head.item == null;Node<E> h = head;Node<E> first = h.next;h.next = h; // help GChead = first;E x = first.item;first.item = null;return x;
}public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();// Note: convention in all put/take/etc is to preset localvar// holding count negative to indicate failure unless set.int c = -1;Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;putLock.lockInterruptibly();try {//当队列满时,调用 notFull.await()方法释放锁,陷入等待状态。//有两种情况会激活该线程//第一、 某个 put 线程添加元素后,发现队列有空余,就调用 notFull.signal()方法激活阻塞线程//第二、take 线程取元素时,发现队列已满。则其取出元素后,也会调用 notFull.signal()方法激活阻塞线程while (count.get() == capacity) {notFull.await();}enqueue(node);c = count.getAndIncrement();//发现队列未满,调用 notFull.signal()激活阻塞的 put 线程(可能存在)if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();
} public E take() throws InterruptedException {E x;int c = -1;final AtomicInteger count = this.count;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lockInterruptibly();try {while (count.get() == 0) {notEmpty.await();}x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;
}public boolean offer(E e) {if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();final AtomicInteger count = this.count;if (count.get() == capacity)return false;int c = -1;Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;putLock.lock();try {if (count.get() < capacity) {enqueue(node);c = count.getAndIncrement();if (c + 1 < capacity)notFull.signal();}} finally {putLock.unlock();}if (c == 0)signalNotEmpty();return c >= 0;
}public E poll() {final AtomicInteger count = this.count;if (count.get() == 0)return null;E x = null;int c = -1;final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;takeLock.lock();try {if (count.get() > 0) {x = dequeue();c = count.getAndDecrement();if (c > 1)notEmpty.signal();}} finally {takeLock.unlock();}if (c == capacity)signalNotFull();return x;
}
ArrayBlockingQueue 和 LinkedBlockingQueue 的区别:
1. 队列大小的初始化方式不同
ArrayBlockingQueue 是有界的,必须指定队列的大小;
LinkedBlockingQueue 是分情况的,指定队列的大小时,就是有界的;不指定队列的大小
时,默认是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,看成无界队列,但当生产速度大于消费速度时候,有可能
会内存溢出。
2. 队列中锁的实现不同
ArrayBlockingQueue 实现的队列中的锁是没有分离的,即生产和消费用的是同一个锁;进
行 put 和 take 操作,共用同一个锁对象。也即是说,put 和 take 无法并行执行!
LinkedBlockingQueue 实 现 的 队 列 中 的 锁 是 分 离 的 , 即 生 产 用 的 是 putLock , 消 费是
takeLock。也就是说,生成端和消费端各自独立拥有一把锁,避免了读(take)写(put)时互
相竞争锁的情况,可并行执行。
3. 在生产或消费时操作不同
ArrayBlockingQueue 基于数组,在插入或删除元素时,是直接将枚举对象插入或移除的,
不会产生或销毁任何额外的对象实例;
LinkedBlockingQueue 基于链表,在插入或删除元素时,需要把枚举对象转换为 Node
进行插入或移除,会生成一个额外的 Node 对象,这在长时间内需要高效并发地处理大批量数
据的系统中,其对于 GC 的影响还是存在一定的区别,会影响性能。
Put()和 take()方法。
都可以实现阻塞的功能。
Put()方法:把元素加入到阻塞队列中,如果阻塞队列没有空间,则调用此方法的线程被阻塞,
直到有空间的时候再继续。
take()方法:取出排在阻塞队列首位的对象,若阻塞队列为空,则调用此方法的线程被阻塞,
直到有新的对象被加入的时候再继续。
offer()和 poll()方法。
不具有阻塞的功能。
offer()方法:把元素加入到阻塞队列中,如果可以容纳,则返回 true。如果不可以容纳,则返
回 false。
poll()方法:取出排在阻塞队列首位的对象,若阻塞队列为空,则返回 null,如果不为空,则返
回取出来的那个元素。
3.PriorityBlockingQueue VSPriorityQueue
此阻塞队列为基于数组的无界阻塞队列。它会按照元素的优先级对元素进行排序,按照优
先级顺序出队,每次出队的元素都是优先级最高的元素。注意,不会阻塞生产者,但会阻塞消
费者。 PriorityBlockingQueue 里面存储的对象必须是实现 Comparable 接口,队列通过这个接
口的 compare 方法确定对象的 priority。
队列的元素并不是全部按优先级排序的,但是队头的优先级肯定是最高的。每取一个头元
素时候,都会对剩余的元素做一次调整,这样就能保证每次队头的元素都是优先级最高的元素。
4.DelayQueue
DelayQueue 是一个无界阻塞队列,用于放置实现了 Delayed 接口的对象,只有在延迟期
满时才能从中提取元素。该队列的头部是延迟期满后保存时间最长的 Delayed 元素。 这个
队列里面所存储的对象都带有一个时间参数,采用 take 获取数据的时候,如果时间没有到,
取不出来任何数据。而加入数据的时候,是不会阻塞的(不会阻塞生产者,但会阻塞消费者)。
DelayQueue 内部使用 PriorityQueue 实现的。 DelayQueue 是一个使用 PriorityQueue
实 现 的 BlockingQueue , 优 先 队 列 的 比 较 基 准 值 是 时 间 。 本 质 上 即 : DelayQueue =
BlockingQueue +PriorityQueue + Delayed。
优势:
如果不使用 DelayQueue,那么常规的解决办法就是:使用一个后台线程,遍历所有对象,
挨个检查。这种笨笨的办法简单好用,但是对象数量过多时,可能存在性能问题,检查间隔时
间不好设置,间隔时间过大,影响精确度,过小则存在效率问题。而且做不到按超时的时间顺
序处理。
应用场景:
缓存系统的设计。缓存中的对象,超过了有效时间,需要从缓存中移出。使用一个线程循
环查询 DelayQueue,一旦能从 DelayQueue 中获取元素时,表示缓存有效期到了。
class Wangming implements Delayed {private String name;// 身份证private String id;// 截止时间private long endTime;public Wangming(String name, String id, long endTime) {this.name = name;this.id = id;this.endTime = endTime;}public String getName() {return this.name;}public String getId() {return this.id;}/*** 用来判断是否到了截止时间*/@Overridepublic long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubreturn endTime - System.currentTimeMillis();}/*** 相互比较排序用*/@Overridepublic int compareTo(Delayed o) {// TODO Auto-generated method stubWangming jia = (Wangming) o;return endTime - jia.endTime > 0 ? 1 : 0;}public class WangBa implements Runnable {private DelayQueue<Wangming> queue = new DelayQueue<Wangming>();public boolean yinye = true;public void shangji(String name, String id, int money) {Wangming man = new Wangming(name, id, 1000 * 60 * money +System.currentTimeMillis());System.out.println("网名" + man.getName() + " 身份证" +man.getId() + "交钱" + money + "块,开始上机...");this.queue.add(man);}public void xiaji(Wangming man) {System.out.println("网名" + man.getName() + " 身份证" +man.getId() + "时间到下机...");}@Overridepublic void run() {// TODO Auto-generated method stubwhile (yinye) {try {System.out.println("检查 ing");Wangming man = queue.take();xiaji(man);} catch (InterruptedException e) {// TODO Auto-generated catch blocke.printStackTrace();}}}public static void main(String args[]) {try {System.out.println("网吧开始营业");WangBa siyu = new WangBa();Thread shangwang = new Thread(siyu);shangwang.start();siyu.shangji("路人甲", "123", 1);siyu.shangji("路人乙", "234", 2);siyu.shangji("路人丙", "345", 3);} catch (Exception ex) {}}
}
5.SynchronousQueue
同步队列是一个不存储元素的队列,它的 size()方法总是返回 0。每个线
程的插入操作必须等待另一个线程的移除操作,同样任何一个线程的移除操作
都必须等待另一个线程的插入操作。可以认为 SynchronousQueue 是一个缓存
值为 1 的阻塞队列。
2. 生产者/消费者问题的多种实现方式
####1.使用阻塞队列实现
// Producer Class in java
class Producer implements Runnable {private final BlockingQueue sharedQueue;public Producer(BlockingQueue sharedQueue) {this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;}public void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {try {System.out.println("Produced: " + i);sharedQueue.put(i);} catch (InterruptedException ex) {System.out.println(ex);}}}
} // Consumer Class in Java
class Consumer implements Runnable {private final BlockingQueue sharedQueue;public Consumer(BlockingQueue sharedQueue) {this.sharedQueue = sharedQueue;}public void run() {while (true) {try {int i = (Integer) sharedQueue.take();System.out.println("Consumed: " + i);} catch (InterruptedException ex) {System.out.println(ex);}}}
}public class ProducerConsumerPattern {public static void main(String args[]) {// Creating shared objectBlockingQueue sharedQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();// Creating Producer and Consumer ThreadThread prodThread = new Thread(new Producer(sharedQueue));Thread consThread = new Thread(new Consumer(sharedQueue));// Starting producer and Consumer threadprodThread.start();consThread.start();}
}2.使用 Object 的 wait()和 notify()实现
PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(10);//充当缓冲区class Consumer extends Thread {public void run() {while (true) {synchronized (queue) {while (queue.size() == 0) {//队列空的条件下阻塞try {queue.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();queue.notify();}}queue.poll(); // 每次移走队首元素queue.notify();}}}
}class Producer extends Thread {public void run() {while (true) {synchronized (queue) {while (queue.size() == 10) {//队列满了的条件下阻塞try {queue.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();queue.notify();}} queue.offer(1); // 每次插入一个元素queue.notify();}}}
}
3.使用 Condition 实现
private PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(10);
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
private Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();class Consumer extends Thread {public void run() {while (true) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == 0) {try {notEmpty.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}queue.poll(); // 每次移走队首元素notFull.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}}
}class Producer extends Thread {public void run() {while (true) {lock.lock();try {while (queue.size() == 10) {try {notFull.await();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}queue.offer(1); // 每次插入一个元素notEmpty.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}}}
}
3. 编程实现一个最大元素为 100 的阻塞队列。
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();Object[] items = new Object[100];int putptr, takeptr, count;public void put(Object x) throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {while (count == items.length)notFull.await();items[putptr] = x;if (++putptr == items.length)putptr = 0;++count;notEmpty.signal();} finally {lock.unlock();}
}public Object take() throws InterruptedException {lock.lock();try {while (count == 0)notEmpty.await();Object x = items[takeptr];if (++takeptr == items.length)takeptr = 0;--count;notFull.signal();return x;} finally {lock.unlock();}
}
4. 设计一个双缓冲阻塞队列,写代码。
在服务器开发中,通常的做法是把逻辑处理线程和 I/O 处理线程分离。
逻辑处理线程:对接收的包进行逻辑处理。
I/0 处理线程:网络数据的发送和接收,连接的建立和维护。
通常逻辑处理线程和 I/O 处理线程是通过数据队列来交换数据,就是生产
者–消费者模型。
这个数据队列是多个线程在共享,每次访问都需要加锁,因此如何减少互
斥/同步的开销就显得尤为重要。解决方案:双缓冲队列。
两个队列,将读写分离,一个给逻辑线程读,一个给 IO 线程用来写,当
逻辑线程读完队列后会将自己的队列与 IO 线程的队列相调换。这里需要加锁的
地方有两个,一个是 IO 线程每次写队列时都要加锁,另一个是逻辑线程在调换
队列时也需要加锁,但逻辑线程在读队列时是不需要加锁的。如果是一块缓冲
区,读、写操作是不分离的,双缓冲区起码节省了单缓冲区时读部分操作互斥/
同步的开销。本质是采用空间换时间的优化思路。
5. Java 中的队列都有哪些,有什么区别。
队列都实现了 Queue 接口。
阻塞队列和非阻塞队列。
阻塞队列:见上面的讲解。
非阻塞队列:LinkedList,PriorityQueue。
搬运工信息
Author:Jason Lou
Email:vip.iotworld@gmail.com
Blog:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21508727
Github:https://github.com/JGPY/JavaGuideBooster
推荐几款学习编程的免费平台
免费在线开发平台(https://docs.ltpp.vip/LTPP/)
探索编程世界的新天地,为学生和开发者精心打造的编程平台,现已盛大开启!这个平台汇集了近4000道精心设计的编程题目,覆盖了C、C++、JavaScript、TypeScript、Go、Rust、PHP、Java、Ruby、Python3以及C#等众多编程语言,为您的编程学习之旅提供了一个全面而丰富的实践环境。
在这里,您不仅可以查看自己的代码记录,还能轻松地在云端保存和运行代码,让编程变得更加便捷。平台还提供了私聊和群聊功能,让您可以与同行们无障碍交流,分享文件,共同进步。不仅如此,您还可以通过阅读文章、参与问答板块和在线商店,进一步拓展您的知识边界。
为了提升您的编程技能,平台还设有每日一题、精选题单以及激动人心的编程竞赛,这些都是备考编程考试的绝佳资源。更令人兴奋的是,您还可以自定义系统UI,选择视频或图片作为背景,打造一个完全个性化的编码环境,让您的编程之旅既有趣又充满挑战。
免费公益服务器(https://docs.ltpp.vip/LTPP-SHARE/linux.html)
作为开发者或学生,您是否经常因为搭建和维护编程环境而感到头疼?现在,您不必再为此烦恼,因为一款全新的免费公共服务器已经为您解决了所有问题。这款服务器内置了多种编程语言的编程环境,并且配备了功能强大的在线版VS Code,让您可以随时随地在线编写代码,无需进行任何复杂的配置。
随时随地,云端编码
无论您身在何处,只要有网络连接,就可以通过浏览器访问这款公共服务器,开始您的编程之旅。这种云端编码的便利性,让您的学习或开发工作不再受限于特定的设备或环境。
丰富的编程语言支持
服务器支持包括C、C++、JavaScript、TypeScript、Go、Rust、PHP、Java、Ruby、Python3以及C#等在内的多种主流编程语言,满足不同开发者和学生的需求。无论您是初学者还是资深开发者,都能找到适合自己的编程环境。
在线版VS Code,高效开发
内置的在线版VS Code提供了与本地VS Code相似的编辑体验,包括代码高亮、智能提示、代码调试等功能,让您即使在云端也能享受到高效的开发体验。
数据隐私和安全提醒
虽然服务器是免费的,但为了保护您的数据隐私和安全,我们建议您不要上传任何敏感或重要的数据。这款服务器更适合用于学习和实验,而非存储重要信息。
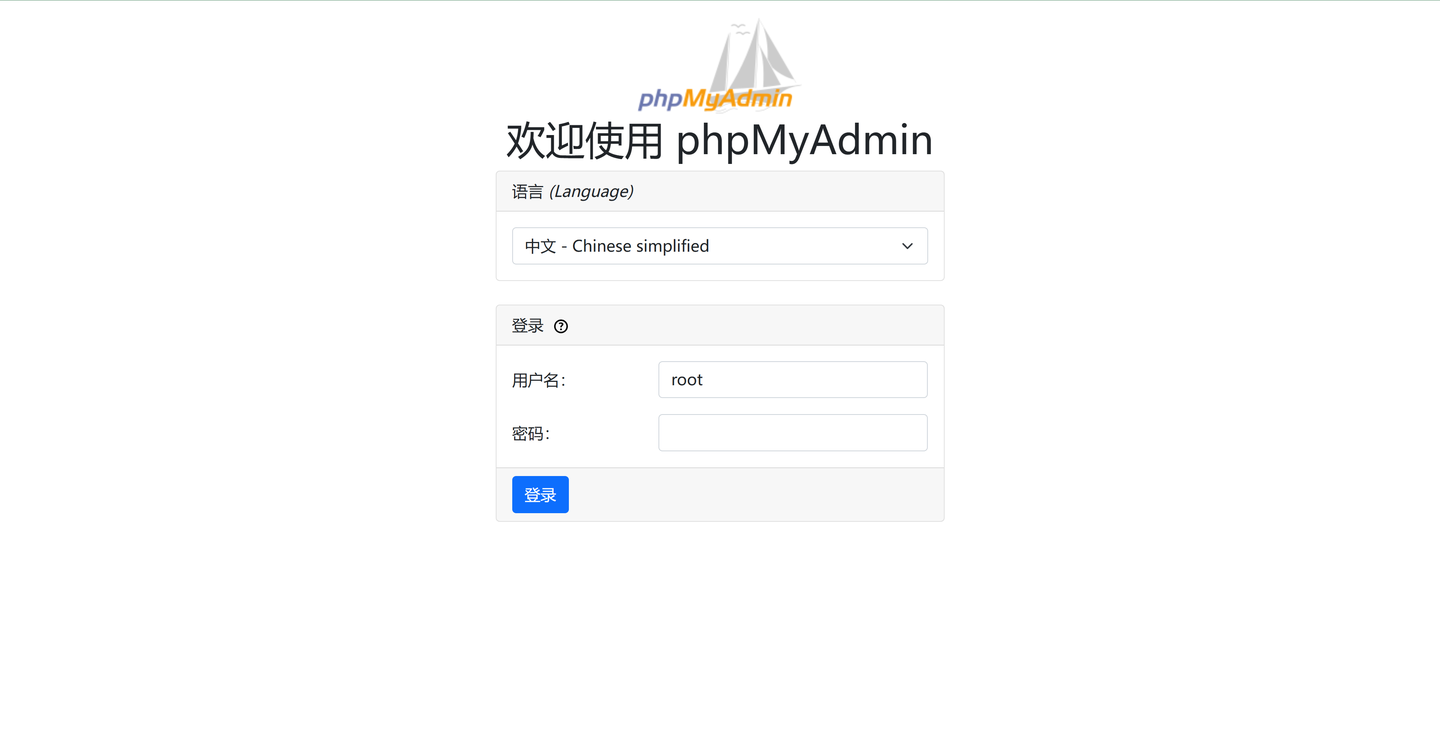
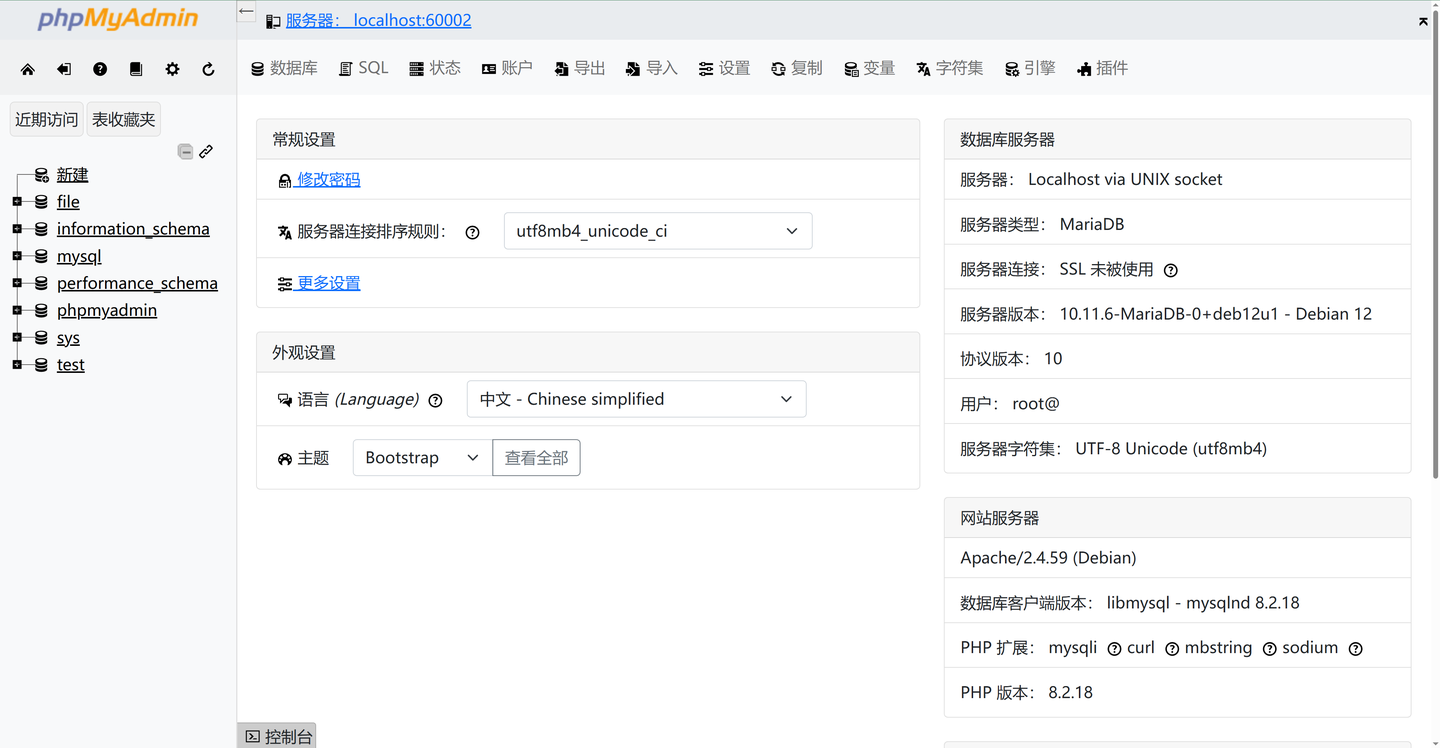
免费公益MYSQL(https://docs.ltpp.vip/LTPP-SHARE/mysql.html)
作为一名开发者或学生,数据库环境的搭建和维护往往是一个复杂且耗时的过程。但不用担心,现在有一款免费的MySQL服务器,专为解决您的烦恼而设计,让数据库的使用变得简单而高效。
性能卓越,满足需求
虽然它是免费的,但性能绝不打折。服务器提供了稳定且高效的数据库服务,能够满足大多数开发和学习场景的需求。
在线phpMyAdmin,管理更便捷
内置的在线phpMyAdmin管理面板,提供了一个直观且功能强大的用户界面,让您可以轻松地查看、编辑和管理数据库。
数据隐私提醒,安全第一
正如您所知,这是一项公共资源,因此我们强烈建议不要上传任何敏感或重要的数据。请将此服务器仅用于学习和实验目的,以确保您的数据安全。
免费在线WEB代码编辑器(https://docs.ltpp.vip/LTPP-WEB-IDE/)
无论你是开发者还是学生,编程环境的搭建和管理可能会占用你宝贵的时间和精力。现在,有一款强大的免费在线代码编辑器,支持多种编程语言,让您可以随时随地编写和运行代码,提升编程效率,专注于创意和开发。
多语言支持,无缝切换
这款在线代码编辑器支持包括C、C++、JavaScript、TypeScript、Go、Rust、PHP、Java、Ruby、Python3以及C#在内的多种编程语言,无论您的项目需要哪种语言,都能在这里找到支持。
在线运行,快速定位问题
您可以在编写代码的同时,即时运行并查看结果,快速定位并解决问题,提高开发效率。
代码高亮与智能提示
编辑器提供代码高亮和智能提示功能,帮助您更快地编写代码,减少错误,提升编码质量。
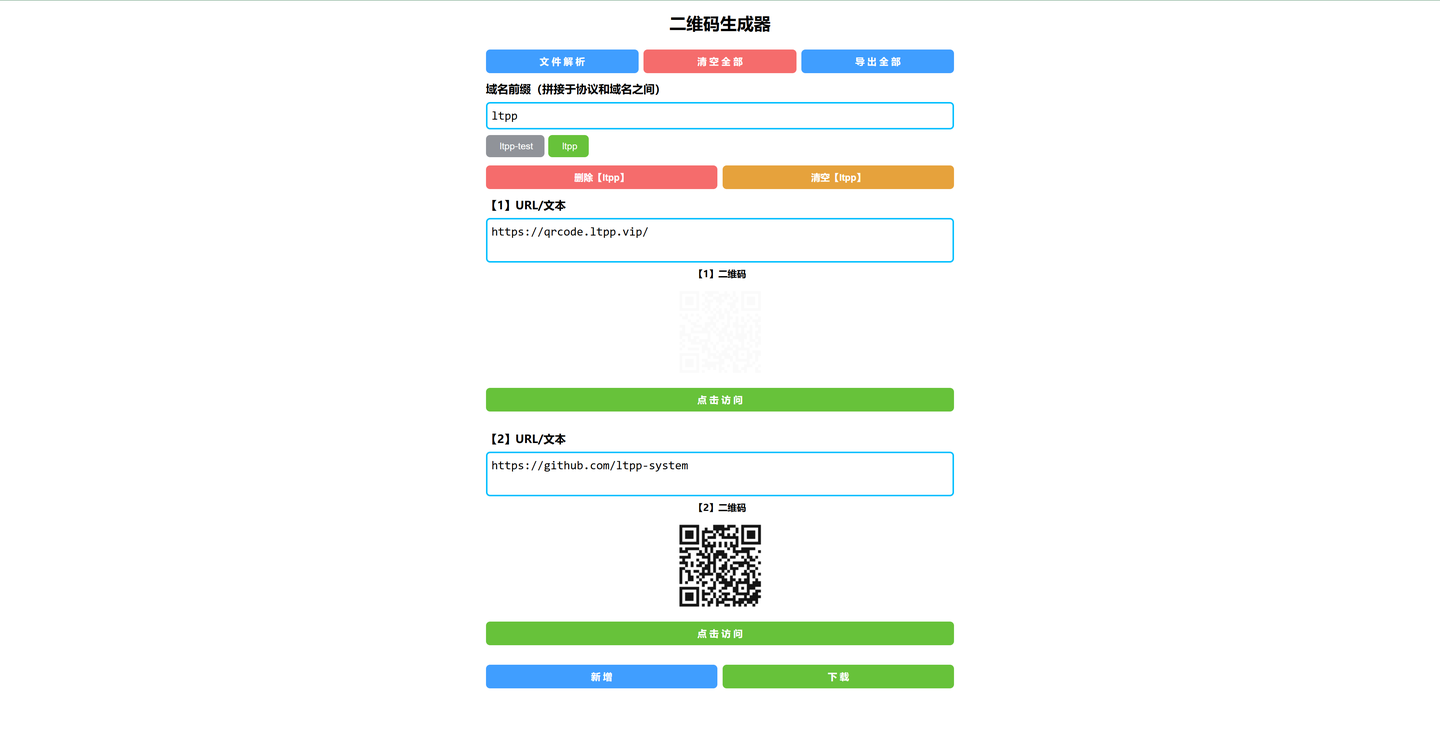
免费二维码生成器(https://docs.ltpp.vip/LTPP-QRCODE/)
二维码(QR Code)是一种二维条码,能够存储更多信息,并且可以通过智能手机等设备快速扫描识别。它广泛应用于各种场景,如:
企业宣传
企业可以通过二维码分享公司网站、产品信息、服务介绍等。
活动推广
活动组织者可以创建二维码,参与者扫描后可以直接访问活动详情、报名链接或获取电子门票。
个人信息分享
个人可以生成包含联系方式、社交媒体链接、个人简历等信息的二维码。
电子商务
商家使用二维码进行商品追踪、促销活动、在线支付等。
教育
教师可以创建二维码,学生扫描后可以直接访问学习资料或在线课程。
交通出行
二维码用于公共交通的票务系统,乘客扫描二维码即可进出站或支付车费。 功能强大的二维码生成器通常具备用户界面友好,操作简单,即使是初学者也能快速上手和生成的二维码可以在各种设备和操作系统上扫描识别的特点。