【初阶数据结构】顺序表和链表算法题(下)
链表
- 2.链表
- 2.4合并两个有序链表
- 2.5链表分割
- 2.6链表的回⽂结构
- 2.7相交链表
- 2.8环形链表I
- 2.9 环形链表II
- 2.10随机链表的复制
2.链表
2.4合并两个有序链表

思路

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* list1, ListNode* list2) {//处理链表为空的情况if (list1 == NULL)return list2;if (list2 == NULL)return list1;//方一代码:创建新的空链表ListNode* newhead = NULL, * newtail = NULL;//list1,list2分别指向两个链表的表头//newhead = newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));while (list1 && list2)//只要有一个条件不满足就跳出循环{if (list1->val < list2->val){//谁小谁尾插if (newhead == NULL){newhead = newtail = list1;}else{newtail->next = list1;newhead = newtail->next;}list1 = list1->next;}else{//l2尾插if (newhead == NULL){newhead = newhead = list2;}else{newtail->next = list2;newtail = newtail->next;}list2 = list2->next;}}//跳出循环只有两种情况,list1为空或list2为空if (list1){newtail->next = list1;}if (list2){newtail->next = list2;}return newhead;
}
//方二代码:创建一个非空链表
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* list1, struct ListNode* list2) {//申请一个动态的空间//此时初始了一个头结点,是个默认的值,最后删掉ListNode* newhead, * newtail;newhead = newtail = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode));while (list1 && list2){//不用判断链表是否为空,直接拿过来尾插if (list1->val < list2->val){newtail->next = list1;list1 = list1->next;}else{newtail->next = list2;list2 = list2->next;}newtail = newtail->next;}if (list1){newtail->next = list1;}else{newtail->next = list2;}ListNode* ret = newhead->next;free(newhead);newhead = NUll;return ret;
}
2.5链表分割

思路

单链表算法题----链表分割
牛客是c++写的
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {// write code hereif (pHead == NULL)return NULL;//创建两个非空链表,小链表和大struct ListNode* lessHead, * lessTail, * greaterHead, * greaterTail;//创建链表表头//注意:我动态开辟空间后 lesshead链表和greathead链表头就有一个默认结点啦lessHead = lessTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));greaterHead = greaterTail = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));//遍历原链表,找小于x的和其它节点尾插导大小链表中struct ListNode* cur = pHead;while (cur){//小于x的尾插到lessTailif (cur->val < x){lessTail->next = cur;lessTail = lessTail->next;}//大于等于x的尾插到greaterTailelse{greaterTail->next = cur;greaterTail = greaterTail->next;}cur = cur->next;}//链接两个链表,小尾结点指向大的下一个结点lessTail->next = greaterHead->next;greaterTail->next = NULL;//获取表头pHead = lessHead->next;free(lessHead);free(greaterHead);return pHead;}
};
2.6链表的回⽂结构

思路

单链表算法题----链表的回⽂结构
/*
struct ListNode {int val;struct ListNode *next;ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {// write code hereif (A == NULL || A->next == NULL)return true;ListNode* slow, * fast, * prev, * cur, * nxt;slow = fast = A;//1.找到中间节点while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;}//此时slow为中间结点 //后半部分逆置(反转链表)prev = NULL;cur = slow;while (cur){nxt = cur->next;cur->next = prev;prev = cur;cur = nxt;}//逐点比对while (A && prev)//此时prev为最后一个结点{if (A->val != prev->val)return false;A = A->next;prev = prev->next;}return true;}
};
2.7相交链表

思路

单链表算法题----相交链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
struct ListNode* getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode* headA, struct ListNode* headB) {ListNode* p1 = headA;ListNode* p2 = headB;int sizeA, sizeB;sizeA = sizeB = 0;while (p1) {sizeA++;p1 = p1->next;}while (p2) {sizeB++;p2 = p2->next;}//求绝对值int gap = abs(sizeA - sizeB);//让长链表先走gap步ListNode* longlist = headA;ListNode* shortlist = headB;if (sizeA < sizeB){longlist = headB;shortlist = headA;}while (gap--){longlist = longlist->next;}//此时,longlist和shortlist在同一起跑线//两种情况 相交,不相交while (longlist && shortlist){if (longlist == shortlist){//链表相交return shortlist;}//继续往后走longlist = longlist->next;shortlist = shortlist->next;}//都走到为空了,链表不相交return NULL;
}
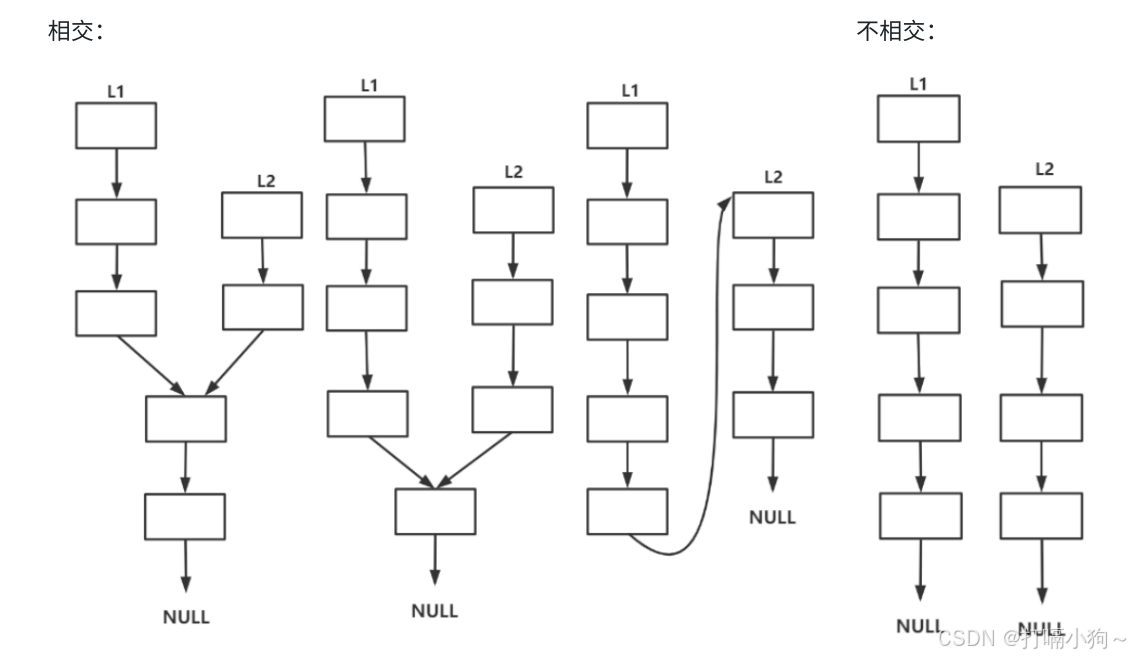
2.8环形链表I

思路证明见下篇


单链表算法题----环形链表I
//判断是否带环
//判断是否相遇,环形链表2下个题是找相遇点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
//走两步
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode* head) {//快慢指针ListNode* slow, * fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast){return true;}}//两个指针始终没有相遇return false;
}
//走三步
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode* head) {//快慢指针ListNode* slow, * fast;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;int n = 3;//fast每次⾛三步while (n--)//进去3次{if (fast->next)fast = fast->next;else//不带环return false;}if (slow == fast){return true;}}//两个指针没有相遇return false;
}
2.9 环形链表II

结论
让⼀个指针(pcur)从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让⼀个指针(next)从判环时相遇点(meet)的位置开始绕环运⾏,两个指针都是每次均走⼀步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。
第一步,找环的相遇点
第二步,从头结点和相遇点开始遍历,每次都走一步
第三步,当pcur和meet相遇时,即入口点
单链表算法题----环形链表II
//先运用找相遇点代码
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* struct ListNode *next;* };*/
typedef struct ListNode ListNode;
ListNode* FindNode(ListNode* head)
{ListNode* fast, * slow;slow = fast = head;while (fast && fast->next){slow = slow->next;fast = fast->next->next;if (slow == fast)return slow;//相遇了}return NULL;
}
struct ListNode* detectCycle(struct ListNode* head) {//找环的相遇点ListNode* meet = FindNode(head);//从头结点和相遇点开始遍历,每次都走一步ListNode* pcur = head;while (meet && pcur){//当pcur和meet相遇时,即入口点if (meet == pcur)return meet;meet = meet->next;pcur = pcur->next;}//链表不带环return NULL;
}
2.10随机链表的复制


思路
第一步,在原链表基础上继续复制链表
第二步,置random指针,copy->random=pcur->random->next
第三步,复制链表与原链表断开
`
`附上几张图便于理解
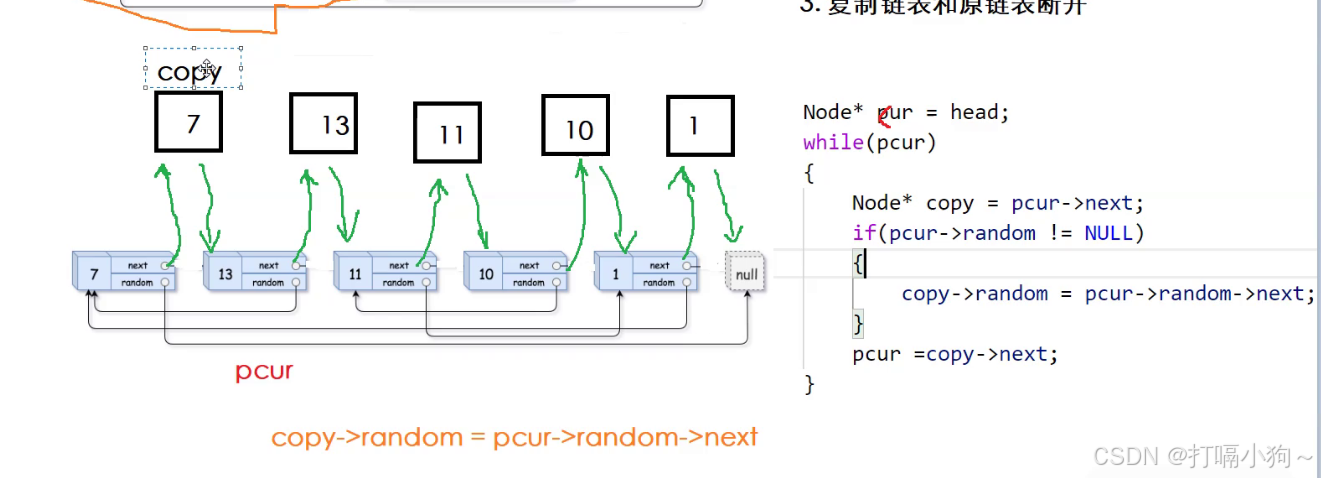
第三步的时候 下图

单链表算法题----随机链表的复制
/*** Definition for a Node.* struct Node {* int val;* struct Node *next;* struct Node *random;* };*/typedef struct Node Node;
Node* BuyNode(int x)
{Node* newnode = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));newnode->val = x;newnode->next = newnode->random = NULL;return newnode;
}
//原链表传过来,复制链表
void AddNode(Node* phead)
{Node* pcur = phead;while (pcur){Node* ret = pcur->next;//创建新节点,尾插到pcur Node* newnode = BuyNode(pcur->val);pcur->next = newnode;newnode->next = ret;pcur = ret;}
}
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {if (head == NULL)return NULL;//第一步AddNode(head);//第二步Node* copy, * pcur, * p1, * newhead, * newtail;pcur = head;newhead = newtail = pcur->next;p1 = pcur;while (pcur){copy = pcur->next;if (pcur->random != NULL){//如果为空,copy->random本来就是null,不用再改了copy->random = pcur->random->next;}pcur = copy->next;}//第三步//让pcur再回到头结点,所以有了p1while (p1->next->next){p1 = p1->next->next;newtail->next = p1->next;newtail = newtail->next;}return newhead;
}
``更多链表算法刷题⼊⼝:
⽜客⽹:https://www.nowcoder.com/exam/oj
LeetCode:https://leetcode.cn/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/description/

